Let’s start with a small trivia. Do you know when was the first computer invented? It was back in the 19th century when the first programmable computer was invented. It is the year 2021 now. Can you imagine your life without a computer or so to say any device? Becoming fully digitalized has become the “motto” for everyone at present. However, this also comes with an added concern. The risk of a data breach. To avoid this sort of vulnerability it is now indispensable to know of ways to protect such information. (Considering data will last longer than systems themselves!). One of the best ways to protect data is to encrypt it. And this is where asymmetric encryption a.k.a “Public key encryption” comes into play.
Through this article, we shall understand asymmetric cryptography (cryptography is the study of techniques like encryption) and the technology behind it. Later, we will also look at scenarios where we use this type of encryption predominantly.
A little pretext…
Before we move to answer the question “what is asymmetric cryptography”, let’s first briefly understand what is encryption in general. In the most non-technical sense, encryption is the process of putting data into a disguise using a set of algorithms. These algorithms convert plaintext data into a form that is unreadable by a computer or a human. To comprehend such data, you would need a special key that would convert this gibberish into normal text.
Below is a pictorial representation of the process of encryption. For further clarity, you can also check out our detailed article on encryption.
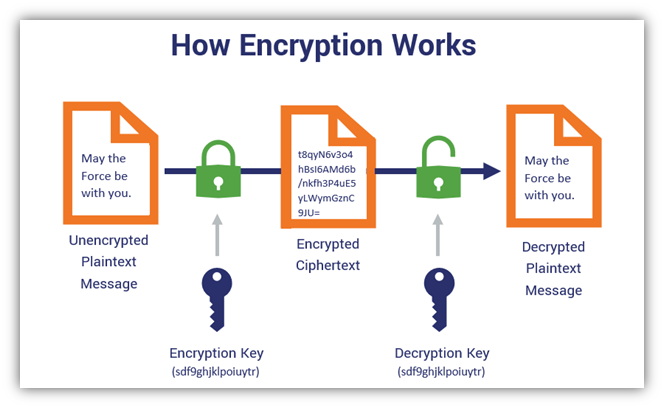
Image Source: https://www.thesslstore.com/blog/symmetric-encryption-101-definition-how-it-works-when-its-used/
What is Asymmetric Cryptography?
Asymmetric encryption is a type of encryption that uses separate keys for encryption and decryption. We call these keys a public key and a private key. The former encrypts data while the latter key decrypts it. This is why we also call asymmetric encryption public-key encryption or public-key cryptography. A key pair for asymmetric encryption is generated from a key generation protocol (a kind of mathematical function) which therefore makes this pair mathematically connected. Together, they’re called a ‘Corresponding Public and Private Key Pair.’
As implied by the name, a private key is used to decrypt already encrypted data. So, only an authorized person, server, machine, or instrument having the private key can have access to the encrypted message/data.
How asymmetric cryptography works in messaging?
Asymmetric cryptography involves two parties – a sender and the receiver; each has its own pair of public and private keys. First, the sender obtains the receiver’s public key (remember the numbers that WhatsApp shows you to confirm end-to-end encryption? Yes, that.).
Subsequently, the plain text is converted to ciphertext. This text is then converted to readable text by the receiver using their private key. Knowing all about the process, the primary benefit of asymmetric cryptography is increased data security.
Asymmetric Cryptography and Internet Security
Asymmetric Encryption is the best option to verify public channels that are insecure and that this is why this type of cryptography is a critical element in the foundation of internet security.
Let’s put this information into use now. Can you see the security lock icon in your browser or HTTPS in the website URL? This indicates that our website uses an SSL Certificate (a digital certificate to validate website identity). What you may not realize here is that you’re actually using public-key encryption right now!
Your browser will do all the work here by extracting a website’s public key from the SSL certificate. Would you like to see a Public Key? Click the lock before the URL and, go to certificate details. This key encrypts any information you send to a website, and then the website’s private key decrypts it. Amazing, isn’t it?
The Foundation for Digital Signatures
At the heart of Digital Signature is asymmetric encryption. A digital signature is the virtual equivalent of a handwritten signature or a seal. We use it specifically to validate the authenticity and integrity of a message. A digital signature is generated using asymmetric encryption and another cryptographic technique called hashing.
In fact, as per Section 3 of the Information Technology Act, 2000, in order to authenticate an electronic record using a digital signature, the authentication must be effected by the use of an asymmetric crypto-system and hash function.
You can refer to this article to learn more about the Indian law on encryption. Be sure to check back over the coming weeks for another article that will focus on digital signatures.
This article was co-authored by Rohit Ranjan Praveer.
Do subscribe to our Telegram channel for more resources and discussions on technology law and news. To receive weekly updates, don’t forget to subscribe to our Newsletter.